CardioTelligence
Headquarter Center
UAE, Duabi
Email Address
Cardiotelligence@gmail.com
Contact Number
(+98)9111861067
Cardiotelligence@gmail.com
Are you Interested in Writing These Articles?
Join Us
The research presented in the case report focuses on the treatment of cardiac and multiorgan hydatid cysts using a combination therapy of albendazole and praziquantel. The case report documents a 35-year-old male patient with recurrent cardiac hydatid cysts and additional cysts in other organs, who showed significant improvement following this combination therapy.
Key Findings and Interpretation
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
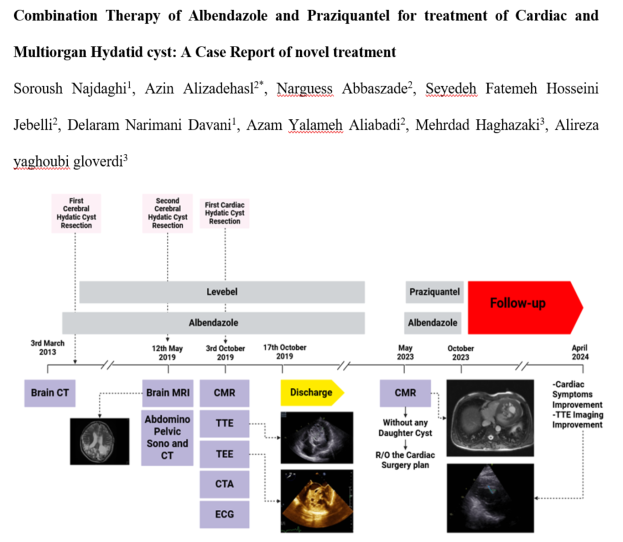
Patient Background: A 35-year-old male with a history of cerebral hydatid cysts presented with dyspnea and chest pain.
Diagnostic Tools: Diagnostic methods included electrocardiogram (ECG), transthoracic echocardiography (TTE), transesophageal echocardiography (TEE), and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR). These tools identified severe left ventricular hypertrophy and large intracardiac cysts.
Medical History: The patient had previously undergone surgeries for cerebral and cardiac hydatid cysts and was treated with albendazole.
Treatment Approach
Combination Therapy: Given the recurrence and the involvement of multiple organs, the patient was treated with a combination of albendazole and praziquantel.
Dosage: Albendazole was administered at 400 mg twice daily, and praziquantel at 40 mg/kg per day twice a week for four weeks, repeated for three courses with a two-week interval between each.
Outcomes
Efficacy: Six months after the initiation of combination therapy, echocardiographic imaging revealed a significant reduction in the size of the cardiac cysts, and the patient's cardiac symptoms improved. The size of the largest cyst reduced to 2.3 × 2.1 cm, and the morphology indicated partial calcification or fibrosis.
Safety: The combination therapy was well-tolerated with no significant adverse effects reported during the treatment and follow-up period.
Key Findings and Interpretation
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
Patient Background: A 35-year-old male with a history of cerebral hydatid cysts presented with dyspnea and chest pain.
Diagnostic Tools: Diagnostic methods included electrocardiogram (ECG), transthoracic echocardiography (TTE), transesophageal echocardiography (TEE), and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR). These tools identified severe left ventricular hypertrophy and large intracardiac cysts.
Medical History: The patient had previously undergone surgeries for cerebral and cardiac hydatid cysts and was treated with albendazole.
Treatment Approach
Combination Therapy: Given the recurrence and the involvement of multiple organs, the patient was treated with a combination of albendazole and praziquantel.
Dosage: Albendazole was administered at 400 mg twice daily, and praziquantel at 40 mg/kg per day twice a week for four weeks, repeated for three courses with a two-week interval between each.
Outcomes
Efficacy: Six months after the initiation of combination therapy, echocardiographic imaging revealed a significant reduction in the size of the cardiac cysts, and the patient's cardiac symptoms improved. The size of the largest cyst reduced to 2.3 × 2.1 cm, and the morphology indicated partial calcification or fibrosis.
Safety: The combination therapy was well-tolerated with no significant adverse effects reported during the treatment and follow-up period.
